Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark, a natural geographic area in the southeast of China, is mainly composed of Mesozoic granite and Paleozoic stratum with rich geosites and unique geological landforms, and is located in the junction of Yangtz Plate and Huaxia Ancient Plate, the southeast of Eurasian Plate and active area of Pacific Plate.
The geopark just like a great work of earth science records 880 million years evolution history of earth and remains valuable geosites of many disciplines such as sedimentology, stratigraphy, paleontology, petrology, geotectology, geodynamics and geomorphology; it preserves valuable and rare biocenosis of 200-million-year evolution history as a original ecological biological park; it keeps granite micro-topography phenomenon of all types, typical characteristics and centralized distribution. It is also a natural museum of granite geological geomorphology and the typical example of world landscape of granite mountains and peaks due to the unique landscape forms and the outstanding natural beauty showed by the magical integration of granite landform, ecology and atmosphere; it owns rich cultural heritage in the 1000-year-joint-development history between humanity and nature, especially that the ancient building sites, created according to Chinese Taoism idea that human is an integral part of nature, are honored as the open-air museum of China Taoism ancient buildings.
Sanqingshan is a precious natural heritage for humankinds. Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark is the typical example of 1000-year harmonious development between human and nature and also a large national geopark founded by Chinese government to protect nature and environment to advance culture and science.

Administrative Division
There are four townshipsand thirty-five villages under administration of the geopark until 2018. Most are Han nationality and less are She nationality. Its population mainly distributes in valleys, river banks and areas along the park. There aren’t residents in park core area.
Sanqingshan is administrated by Shangrao City of Jiangxi Province and is located in northeast of Jiangxi Province and the junction of Dexing City and Yushan County, known as Notable Town of Southeast of China in ancient times and intersection of Rao, Xin and Qu.
During the Spring and Autumn Period and the Warring State Period, Sanqingshan was under the administration of Wu, Yue and Chu sequentially while under the administration of Jiujiang Shire in Qin Dynasty, and Yuzhang Shire in Han Dynasty and under Wu in the Three Kingdoms Period. After the national unification in Sui Dynasty, it was administrated by Yiyang County of Poyang Shire. In 695 of Tang Dynasty, Wuzetian Empress established Yushan County that administrated Sanqingshan. After Song Dynasty, Sanqingshan was mainly administrated by Yushan County. After October of 1949, it is administrated by Yushan County and Dexing County.
In 1984, the administrative bureau of Sanqingshan Scenic Area at county level was founded. In February of 1995, Jiangxi Provincial Government approved to set up Sanqingshan Tourism & Economic Development Zone and the administrative committee of development zone was also founded. In 1996, Shangrao Party Committee and administrative office approved to establish the Administrative Committee of Sanqingshan Scenic Area. In 2005 the National Geopark was approved and established, and in 2009 the Administrative Committee of Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark at county level.

Location and Traffic
Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark is situated at the junction of Yushan County and Dexing City within the region of Shangrao City, Jiangxi Province.
The Geopark covers a total area of 433 square kilometer.It is 53.8 km away from Yushan County to the south, 97.9 km away from Shangrao City, 96.8 km away from Dexing City to the west and 76 km away from Wuyuan County to the north.
Geographical coordinates: 28°48′22″~29°00′42″N, and 117°58′ 20″~118°08′28″E.
Sanqingshan is located at the junction of Jiangsu and Zhejiang, near pear Wen Expressway (Shangrui 311 high-speed), Jing Wu often two highway and 320 national highway, constitute criss crossing the highway transportation network, Zhejiang Jiangxi railway connected around, Jingdezhen airport, Zhejiang Quzhou airport building air corridor. Road, rail, air transport to make Mount Sanqingshan tourism initially formed a three-dimensional transportation network.
Note: Liwen freeway refers to Shangrui 311 highways (Shanghai to Ruili Expressway) in Jiangxi Province, the eastern section of the East Yushan County, the pear orchard, connected with the highway in Quzhou, Zhejiang Province to the kiln, West to Jinxian County of Jiangxi Province Wen Jia Zhen, is connected with the Jiangxi Province good-natured highway, across the Shangrao, Fuzhou, Nanchang three design district city, 245 km in length.

Hydrological Characteristics
Sanqingshan is located in the headstream of Xinjiang River Basin of the Poyang Lake in the middle course of Yangtze River and the Qiantang River. River systems in the south of the park mainly flow into Poyang Lake through Xinjiang River and An’le River while river systems in the north of the park mainly flow into Qiantang River and the East China Sea. The surface water here is mainly valley stream and its primary source is rainwater. The surface water resource here differs distinctively in different seasons that in rainy seasons it is plentiful while in dry seasons it is insufficient. Because there are many fissures between bedrocks, with strong water permeability, part of rainwater could directly permeate into these fissures and turns into underground water (tectonic fissure water). In all rocks with fissures there is rich water which offers favorable conditions for vegetation around the whole mountain. In shallow pits areas and gentle slopes, the weathering rock scraps and clay substance are in patchy distribution which more is pore infiltration water.
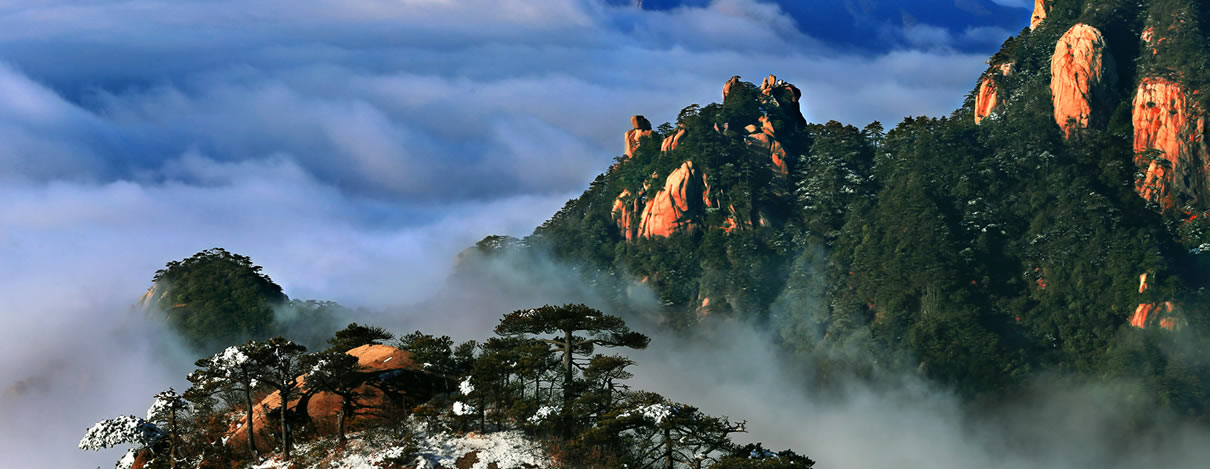


Climate Characteristics
Climate
The geopark is 340 km away from the East China Sea. With the influence of oceanic climate, here is subtropical monsoon climate with mountain climate features affected by altitude.
Temperature
There’re four distinctive seasons with a cool and humid summer and a long winter. The winter is from the middle of October to later April of next year; the spring is from late April to June; the summer is from July to August; the autumn is from September to early October. The average temperature yearly in Sanqingshan is 10.9℃ while average temperature in July is 21.2℃, the highest temperature in July and August is 33℃ and the lowest temperature in January is -16.0℃. The average annual precipitation here is 1857.7 mm and the average annual evaporation is 1331.6 mm. The average annual relative humidity is 82%.


Development
Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark was approved as the National Geopark by Ministry of Land and Resources and started to declare the Global Geopark in September,2015
March 3, 2007, Sanqingshan National Geopark held the inaugural opening formally and officially.
In 2006, as the application units, Shanqingshan was listed as the application subject of China Global Natural Heritage by Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development while Longhushan was recommended to Ministry of Land and Resources as the application subject of Global Geopark by People’s Government of Jiangxi Province with the consideration of the provincial general situation of tourism development.
January 2010, Shanqingshan and Kanas of Xinjiang were listed as the application units of 2012 China Global Geopark by Ministry of Land and Resources on the 4th Recommendation Conference of Global Geopark Application Units held in Beijing.
August 2011, the full set application documents of Shanqingshan were submitted to Ministry of Land and Resources with the approval of People’s Government of Jiangxi Province. October 2011, Shanqingshan Party Committee and Management Committee setup the leading group to do preparations to pass the testing and launched overall works for the application.
November 30, 2011, Shanqingshan opened the special meeting to drive the preparation works and renovation works for the application of Global Geopark and issued < Program on Environment Improvement for the Application of Global Geopark>.
December 2011, documental materials were submitted to UNESCO to investigate.
September 21, 2012, Shanqingshan was listed as Member of the Global Geoparks by UNESCO in the 11th Global Geopark Conference held in Aloka of Portugal.

Sanqingshan Global Geopark established the ties of “sister geopark”
with Lesvos Island Global Geopark of Greece in September 2012,
and with Lushan Global Geopark of China on May, 31 2013,
and with Zhangjiajie Global Geopark of China in March 2014;
and with Villuercas Ibores Jara Global Geopark of Spain in April 2015,
and with Stonehammer Global Geopark of Canada in August 2015,
and with Zhijindong Global Geopark of China in October 2015,
and with Longhushan Global Geopark of China in March 2016,
and with Wangwushan-Daimeishan Global Geopark of China in September 2017,
and with Tianzhushan Global Geopark of China in August 2018,
and with Yandangshan Global Geopark of China in March 2019,
and with Leye-Fengshan Global Geopark of China in October 2020.
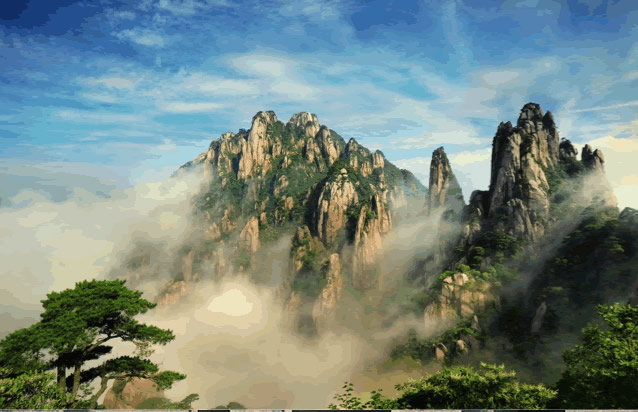


Animal and Plant

Animal resources
The park’s animal geographic division belongs to eastern hilly and plain subregion of Central China Region in Sino-India subkingdom of Oriental Realm. Because of its complex habitat in the mountain climate and the permeation of parts of Palearctic species, the fauna here is featured that Oriental species are principal and the Palearctic species are minor. Based on resource investigation in 1982, there’re over 300 kinds of species such as various birds, beasts, insects and amphibians. There’re many national rare animals, such as silver pheasant, owl, pagolin, stump-tailed macaque, selenarctos thibetanus and micichthys miiuy those are Second Class national protected animals, and panthera pardus and rusa those are First Class national protected animals.
Among vertebrates and insects of Sanqingshan, there are 21 species listed in IUCN Red List (2003) such as clouded leopard, leopard, tufted deer, macaque, macaca thibetana, manis pentadastyla, jackal, black bear, golden cat, river deer, serow, micromys minutus, porcupine, tragopan caboti, syrmaticus ellioti, grey-headed lapwing(2002), bombycilla garrulus, rhinomyias brunneatus, platyternon, tortoise and trionyx sinensis.
Plant resources
The park is located in the eastern part of mid-subtropical area and belongs to Eastern China Area of Sino-Japan Subregion of Holarctic Region. With the warm and wet climate, sufficient sunshine, abundant rainwater and multiple terrains, there’re plenty plant species here. The found out higher plant in the park are 2373 species those belong to 253 families and 984 species. Among them, there are bryophyte of 326 species, 165 genera and 65 families, ferns of 179 species, 71 genera and 34 families, gymnosperm of 24 species, 22 genera and 6 families and angiosperm of 1802 species, 726 genera and 148 families. Here grows not only abundant plants of evergreen broad-leaf forest zone in China mid-subtropical areas but also pinacease pseudotsuga plants, especially it is the distribution center of pseudotsuga gaussenii in the world.
Plant resources
In the park there’re 68 genera of East Asian-North America intercontinental disjunctive distribution plants which is 56.2% of such genus in China. This means that Sanqingshan is not only the core area of East Asian-North America discontinuous flora, but also one of the important distribution centers of Este Asian plants. The planting area of pseudotsuga gaussenii reaches 533 hectares and is the largest of East China. Furthermore, the prosperous and stable community of pseudotsuga gaussenii declares that it is the best place to discuss and investigate pinacease migration genesis research of the cradle geosites of North America flowering fir evolution.
In the core area of Sanqingshan, with abundant diversity of species, there’re many characteristic and endemic species and the formed various kinds of characteristic plant communities, called as the corridor of species and ecological wonders. Up along the aerial walkway in the west coast, there’re various characteristic species in order such as Rhododendron simiarum, Pinus taiwanensis, Cyclobalanopsis glauca, Schima superba, Sorbus pohuashanensis, Lindera obtusiloba, pepperbush, Sorbus folgneri, Litsea cubeba and Lisea coreana in low elevation area, rare and endangered species in medium elevation area such as Magnolia cylindrical, Taxus chinensis var mairei, pseudotsuga gaussenii and fokienia hodginsii and in high elevation area such as Pinus taiwanensis Hayata, pseudotsuga gaussenii, castanopsis sclerophylla schott, chinese enkianthus, pepperbus and Yuanshanian fargesia.






















































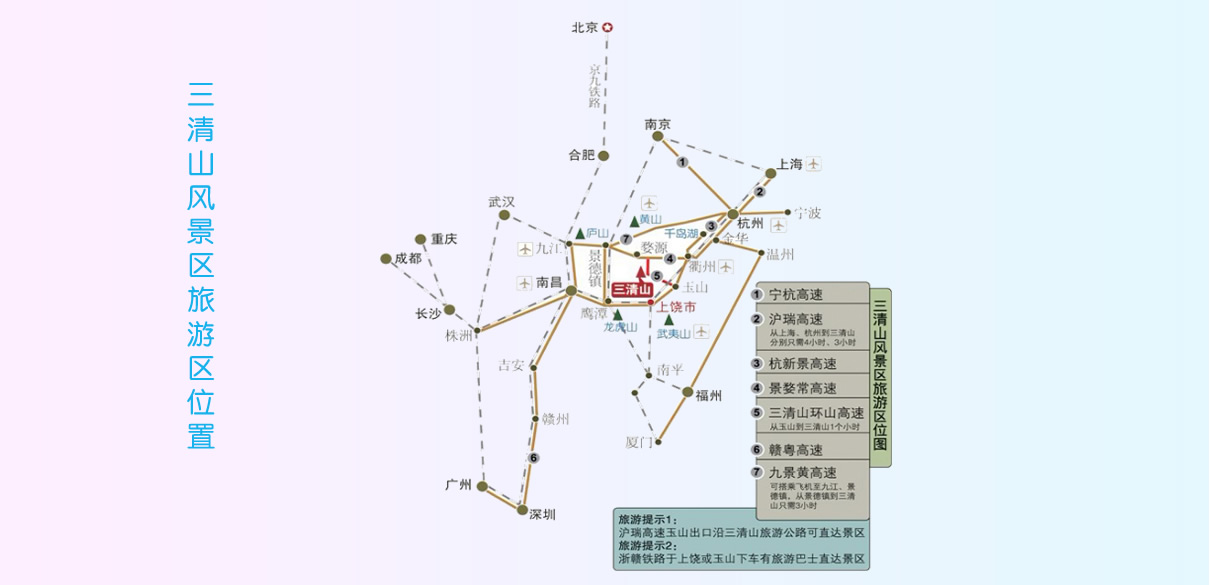

















 赣公网安备 36110202000032号
赣公网安备 36110202000032号