
-
- ◆ We will take you to Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark
- ◆ Activities held in Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark on World Earth Day
- ◆ Guangwushan-Nuoshuihe in Sichuan Provicne and Dabieshan in Hubei have been listed in GGN
- ◆ Cleaner Volunteering Program for Sanqingshan
- ◆ The 2018 Sanqingshan Guide Training Concluded with a Great Success
- ◆ 2018 Third SKYTRAIL® Sanqingshan Cross-country Race Competition
- ◆ The Notice of Extension of the Sanqingshan Geopark’s Closure
- ◆ Strategic Partnership has been signed between the Administrative Committee of Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark and Shangrao Normal University
- ◆ Notice: Sanqingshan will close from Jan 28th to 30th, 2018.
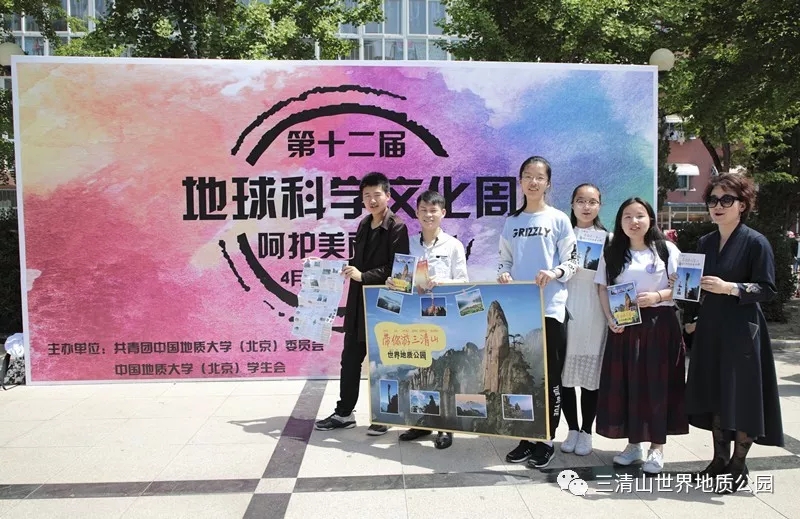

We will take you to Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark
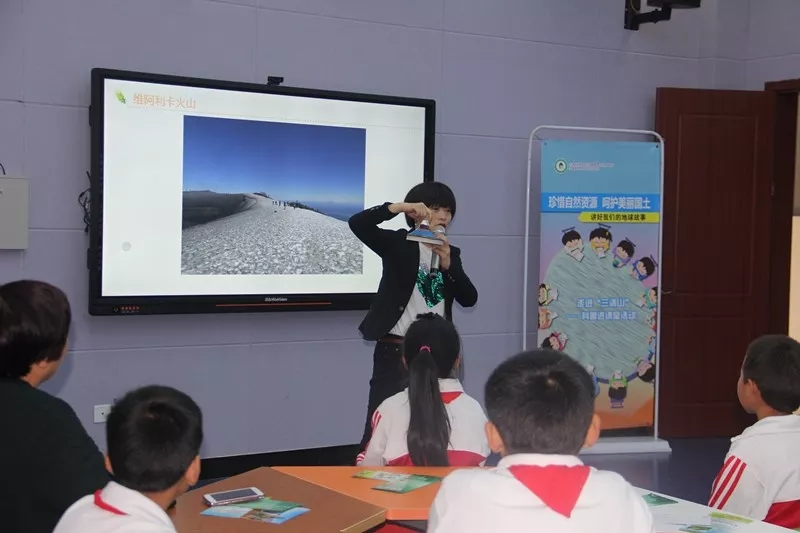

Activities held in Sanqingshan UNESCO Global Geopark on World Earth Day
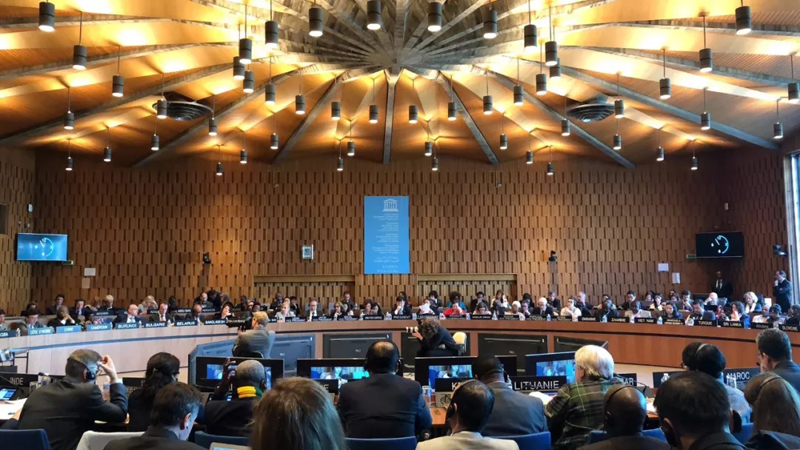

Guangwushan-Nuoshuihe in Sichuan Provicne and Dabieshan in Hubei have been listed in GGN
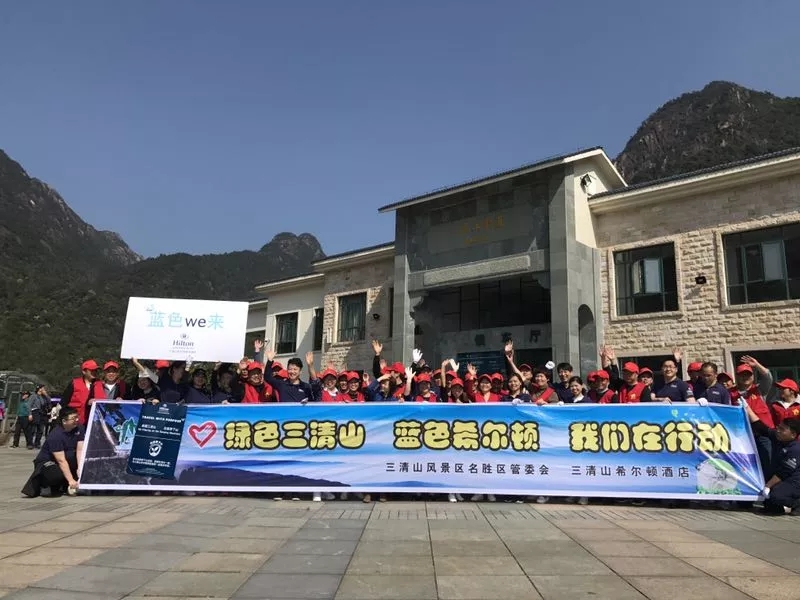

Cleaner Volunteering Program for Sanqingshan
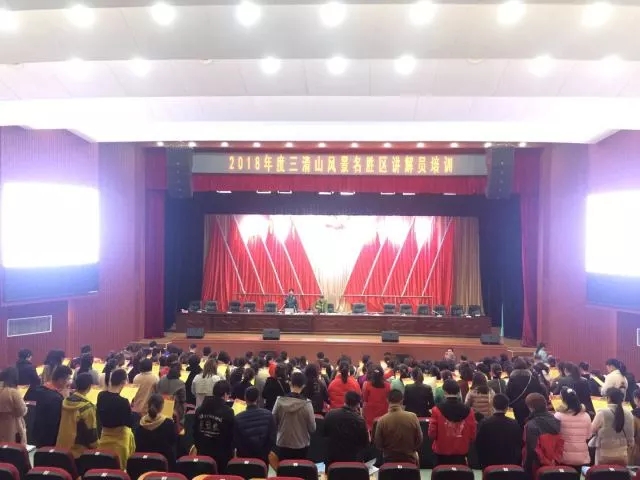

The 2018 Sanqingshan Guide Training Concluded with a Great Success

2018 Third SKYTRAIL® Sanqingshan Cross-country Race Competition




























 赣公网安备 36110202000032号
赣公网安备 36110202000032号